|
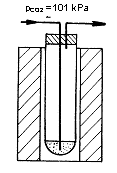
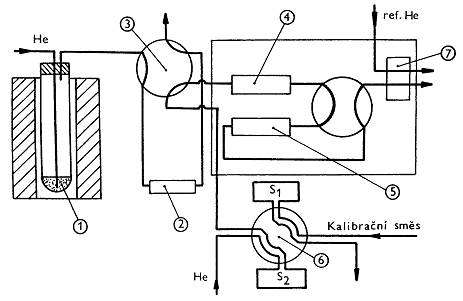
Determination of the solubility of gases in the glass melt consists of two steps. In the first step, the melt flows are saturated using the pure gas. After reaching equilibrium, the melt is rapidly cooled to room temperature. The concentration of dissolved gas is then determined by the gas chromatographic method described below. The principle of the determination of gases dissolved in the glass melt is the continuous extraction of the dissolved gas from the melt by the flow of inert gas and subsequent chromatographic analysis of the released gases. The analyzed glass sample in the form of a 5 x 5 x 10 mm rectangular block is placed in a quartz glass tube inserted in a laboratory tube furnace heated to 1500 ° C. At the bottom of the test tube, helium flows through quartz capillary. Released gases are captured in a concentration loop immersed in liquid nitrogen. After completion of the extraction (60 minutes), the loop is quickly heated by immersion in hot oil and transferred to the carrier gas circuit of the chromatograph. The determination method allows the simultaneous determination of carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur dioxide. Other dissolved gases, such as water vapor or argon, cannot be determined in this arrangement. |
|
 |
 |
|
Figure: Measuring instruments for gas analysis in melts |
Figure: Schematics of saturation of melt by gas |
|
Diagram of apparatus for determining gases in the melt
|
 |
Solubilities of gases in melts
Updated: 14.12.2017 22:25, Author: Richard Pokorný
