|
The Redox state expresses the relationship between the oxidation forms of transition metal present in the melt, mainly iron, chromium and other elements. The redox state controls the resulting glass color, the value of the effective thermal conductivity, and the bubble removal process (refining process). The redox state of the melt is also important in calculations of the distribution of oxidation-reducing components in glass melting furnaces or in bubble nucleation. The commercially available method of measuring the redox state of glass is the Rapidox system. The method is based on electrochemical measurement of the equilibrium voltage between the reference and the measuring electrode. The measuring electrode is a Pt or Ir wire. The reference electrode is located in a Ni / NiO mixture which guarantees a defined partial pressure of oxygen. From the measured value of electromotive voltage E (V), the partial pressure of oxygen is calculated using the Nernst equation. |
|
 |
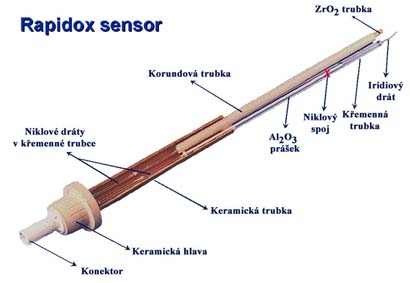 |
| Figure: RAPIDOX system | Figure: Measuring probe |
Oxygen partial pressure in melts
Updated: 26.12.2017 21:02, Author: Richard Pokorný
